 I like to start the semester with a “ripped from the headlines” case. This is especially helpful if some of one’s cases are older. This semester, Zoom is a great alternative. The current market capitalization is about $80B which puts it well above many more established companies (including the combined value of the 7 largest airlines). I have compiled a short packet of news articles for the case. In addition, I have created a spreadsheet that guides students through key scenarios and how they would affect the value of the company (Do rivals match on quality? Is there a price war, Does Zoom keep innovating?). This highlights how qualitative analysis affects assumptions in quantitative models. It is also an introduction to decision trees as a simple tool for modeling complex sources of uncertainty (this is available in a separate instructor spreadsheet that uses PrecisionTree to model the uncertainty). The Zoom context hits just about every key aspect of a strategy course so you can circle back to it repeatedly:
I like to start the semester with a “ripped from the headlines” case. This is especially helpful if some of one’s cases are older. This semester, Zoom is a great alternative. The current market capitalization is about $80B which puts it well above many more established companies (including the combined value of the 7 largest airlines). I have compiled a short packet of news articles for the case. In addition, I have created a spreadsheet that guides students through key scenarios and how they would affect the value of the company (Do rivals match on quality? Is there a price war, Does Zoom keep innovating?). This highlights how qualitative analysis affects assumptions in quantitative models. It is also an introduction to decision trees as a simple tool for modeling complex sources of uncertainty (this is available in a separate instructor spreadsheet that uses PrecisionTree to model the uncertainty). The Zoom context hits just about every key aspect of a strategy course so you can circle back to it repeatedly:
- What is Zoom’s strategy? I use the strategy diamond framework (arena, vehicles differentiators, staging/pacing…) but one can use a standard set of questions to explore this.
- Trends/PEST. The industry was growing at about 10% — what were the drivers of this and how will this change in the future?
- Industry analysis:
- Why was the videoconferencing market attractive (pre-COVID)? (e.g., network effects, value produced)
- How did COVID change the market attractiveness?
- Rivalry: Competitors like Microsoft and Cisco are putting substantial resources into their products. Will they match the quality? Will there be a price war?
- Evolution: How will the industry change going forward?
- Resources and Capabilities:
- Why has Zoom been so successful even before the COVID pandemic?
- Why has Zoom been more effective than rivals during the pandemic?
- Will they be able to keep up the rate of innovation after COVID?
- Corporate strategies. Do business portfolios confer an advantage to rivals?
- Consider Microsoft’s complementary assets (e.g., MS Office) – Why might they be important?
- Consider Cisco’s complementary assets (e.g., enterprise networks) – Why might they be important?
- Zoom has entered the hardware industry through multiple alliances with DTEN, Poly, NEAT and others. Evaluate both the strategy to enter the hardware arena and the vehicle (alliances).
- Zoom’s global strategy? Zoom has operations all over the world. What is their global strategy? Is it sound?
- Technology/Entrepreneurship. Of course, these are key aspects of the context. Why did Zoom CEO, Eric Yuan, leave WebEx? Why did his nascent company do so well against established, well-resourced, rivals.
There are many videos you can bring into this including (Thanks to Rich Makadok for suggestions):
- How Microsoft Ruined Skype (11 min)
- Zoom company story: How Eric Yuan defeated Skype (11 min)
- Lots of zoom humor on youtube…
Contributed by Russ Coff

 Much of the news focuses on how hard businesses have been hit by the pandemic. However, strategy is about finding opportunities and adapting in a dynamic environment. Let’s not forget to focus on inspirational examples along these lines. Send students on a scavenger hunt (like the
Much of the news focuses on how hard businesses have been hit by the pandemic. However, strategy is about finding opportunities and adapting in a dynamic environment. Let’s not forget to focus on inspirational examples along these lines. Send students on a scavenger hunt (like the  I have taught during numerous crises (various wars, 911, 2008 crash, etc.) and always regretted missing opportunities to bring the events into the classroom. So how can we encourage our students to think strategically about the COVID crisis? Here are a few ideas for discussion or team projects (but
I have taught during numerous crises (various wars, 911, 2008 crash, etc.) and always regretted missing opportunities to bring the events into the classroom. So how can we encourage our students to think strategically about the COVID crisis? Here are a few ideas for discussion or team projects (but 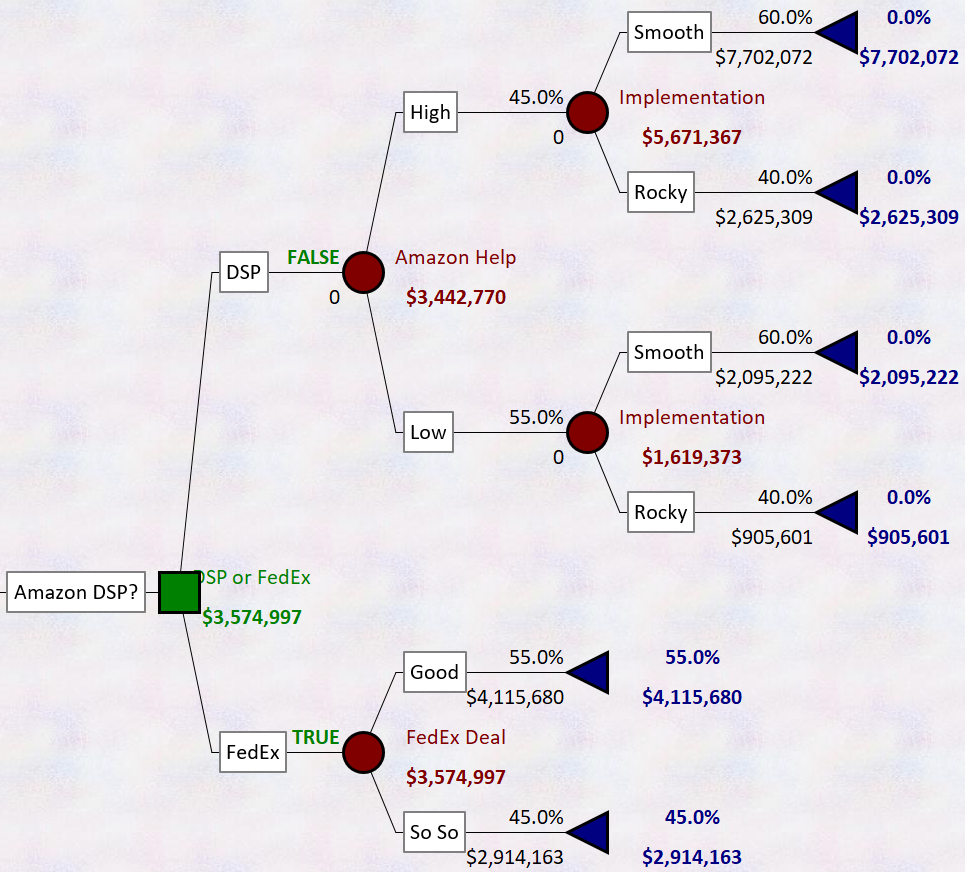 Amazon is encouraging employee spinouts. They are offering employees $10,000 plus 3 months salary to quit and form entrepreneurial ventures in their
Amazon is encouraging employee spinouts. They are offering employees $10,000 plus 3 months salary to quit and form entrepreneurial ventures in their  This 45-minute exercise can be used in a range of management courses and works well in almost any size class. Students are divided into two groups (managers and workers) that must cooperate to produce a re-organization (a simple seating chart). However, managers discover that workers are reluctant to move and about 90% of classes fail to achieve the task. This generates a lively discussion on what is required to lead change, as well as on topics such as communication, trust, power, and motivation. I just ran this for the first time and, to my surprise, the students were successful. However, in the process, it was clear that there were moments of distrust within and between groups. A last person held out to see if he could appropriate more value. In the end, the management team gave up all value that was created. That is, employees appropriated all of the value and managers actually lost money in the exercise. It was quite successful and students thanked me for the experience. All of the details needed to run the exercise are in the article at the link above and it was easy to set up and run.
This 45-minute exercise can be used in a range of management courses and works well in almost any size class. Students are divided into two groups (managers and workers) that must cooperate to produce a re-organization (a simple seating chart). However, managers discover that workers are reluctant to move and about 90% of classes fail to achieve the task. This generates a lively discussion on what is required to lead change, as well as on topics such as communication, trust, power, and motivation. I just ran this for the first time and, to my surprise, the students were successful. However, in the process, it was clear that there were moments of distrust within and between groups. A last person held out to see if he could appropriate more value. In the end, the management team gave up all value that was created. That is, employees appropriated all of the value and managers actually lost money in the exercise. It was quite successful and students thanked me for the experience. All of the details needed to run the exercise are in the article at the link above and it was easy to set up and run. The Alphabet Soup
The Alphabet Soup Strategy classes often give short shrift to managing change but this is where the rubber hits the road.
Strategy classes often give short shrift to managing change but this is where the rubber hits the road.  Some fear that eventually and robots will be
Some fear that eventually and robots will be  Generic strategies are easy enough to explain and students typically feel that they understand. But do they really? Could they develop and implement a sound strategy? Sometimes it’s worth a bit of additional hands-on experience to make sure the lessons stick. Probably the most important message is alignment — the need to design the organization and product to fit the strategy. In other words, to make the appropriate tradeoffs.
Generic strategies are easy enough to explain and students typically feel that they understand. But do they really? Could they develop and implement a sound strategy? Sometimes it’s worth a bit of additional hands-on experience to make sure the lessons stick. Probably the most important message is alignment — the need to design the organization and product to fit the strategy. In other words, to make the appropriate tradeoffs.  With its $13.7B bid, Amazon agreed to pay a 27% premium over Whole Foods’ previous market valuation. This makes for a nice live case case in your strategy classroom. Was this a sound business decision? The market rewarded Amazon with an increase in its stock price. While some opportunities are apparent, it remains unclear exactly how Whole Foods will be worth 27% more to Amazon (and that’s just to break even). A five forces analysis will reveal that the grocery market is highly competitive with exceptionally thin margins — not an especially attractive industry to enter. So how can they win in this game? There are many possibilities that may come up in a discussion. For example, Amazon may:
With its $13.7B bid, Amazon agreed to pay a 27% premium over Whole Foods’ previous market valuation. This makes for a nice live case case in your strategy classroom. Was this a sound business decision? The market rewarded Amazon with an increase in its stock price. While some opportunities are apparent, it remains unclear exactly how Whole Foods will be worth 27% more to Amazon (and that’s just to break even). A five forces analysis will reveal that the grocery market is highly competitive with exceptionally thin margins — not an especially attractive industry to enter. So how can they win in this game? There are many possibilities that may come up in a discussion. For example, Amazon may: Strategies rarely work out as planned but somehow, students remain eternally hopeful that everything will go exactly as they expect. This experiential exercise allows students to “feel”
Strategies rarely work out as planned but somehow, students remain eternally hopeful that everything will go exactly as they expect. This experiential exercise allows students to “feel”  Inflate ball & sit on it. Ask 2 volunteers to inflate a heavy duty inflatable ball using a small air pump (one can buy these a sport store) and try to sit on it afterwards for a minute. While introducing the exercise, the instructor should keep the plug hidden in her/his pocket. Inflating the ball is amusing (both the volunteers and the audience). It is not easy or quick to inflate the ball.
Inflate ball & sit on it. Ask 2 volunteers to inflate a heavy duty inflatable ball using a small air pump (one can buy these a sport store) and try to sit on it afterwards for a minute. While introducing the exercise, the instructor should keep the plug hidden in her/his pocket. Inflating the ball is amusing (both the volunteers and the audience). It is not easy or quick to inflate the ball. takes the plug out admitting that she/he had it all the time. The class will laugh. It may be frustrating for the volunteers but then we begin the debrief and explain the reason for the deception in the exercise.
takes the plug out admitting that she/he had it all the time. The class will laugh. It may be frustrating for the volunteers but then we begin the debrief and explain the reason for the deception in the exercise. This is another in our series of explorations in
This is another in our series of explorations in  This isn’t the first time polls have been wrong. The election of Donald Trump was a shock to many college students (as well as the press) and this may warrant some class time. Some instructors responded by
This isn’t the first time polls have been wrong. The election of Donald Trump was a shock to many college students (as well as the press) and this may warrant some class time. Some instructors responded by  What follows is a brief description/outline of the lecture. While it certainly won’t do it justice, it may offer some important ideas for instructors to explore.
What follows is a brief description/outline of the lecture. While it certainly won’t do it justice, it may offer some important ideas for instructors to explore. Managing change is given little time in most strategy courses. We often understate how difficult strategic change actually is and then wonder why organizations struggle so much with implementation (and our students think its all common sense). You can think of it as walking blindfolded on a tightrope between two solid foundations. During the transition, there is great uncertainty about whether the desired path is attainable. This, of course, is another way of looking at Lewin’s unfreeze/change/refreeze model. This video can help to illustrate the issue:
Managing change is given little time in most strategy courses. We often understate how difficult strategic change actually is and then wonder why organizations struggle so much with implementation (and our students think its all common sense). You can think of it as walking blindfolded on a tightrope between two solid foundations. During the transition, there is great uncertainty about whether the desired path is attainable. This, of course, is another way of looking at Lewin’s unfreeze/change/refreeze model. This video can help to illustrate the issue:

 Ive “worked closely with the late co-founder Steve Jobs, who called Mr Ive his spiritual partner on products stretching back to the iMac.” As before, the reliance on a single person in this role raises key questions: An article published in the New Yorker earlier this year described how “Mr Ive had been describing himself as both ‘deeply, deeply tired‘ and ‘always anxious’ and said he was uncomfortable knowing that ‘a hundred thousand Apple employees rely on his decision-making – his taste – and that a sudden announcement of his retirement would ambush Apple shareholders.‘” Can this be described as an organizational capability? An organizational routine? A dynamic capability? Does it matter that the capability is largely embedded in a single person who is not an owner? All good questions to kick off a nice class discussion…
Ive “worked closely with the late co-founder Steve Jobs, who called Mr Ive his spiritual partner on products stretching back to the iMac.” As before, the reliance on a single person in this role raises key questions: An article published in the New Yorker earlier this year described how “Mr Ive had been describing himself as both ‘deeply, deeply tired‘ and ‘always anxious’ and said he was uncomfortable knowing that ‘a hundred thousand Apple employees rely on his decision-making – his taste – and that a sudden announcement of his retirement would ambush Apple shareholders.‘” Can this be described as an organizational capability? An organizational routine? A dynamic capability? Does it matter that the capability is largely embedded in a single person who is not an owner? All good questions to kick off a nice class discussion…